38 longitudinal wave labled
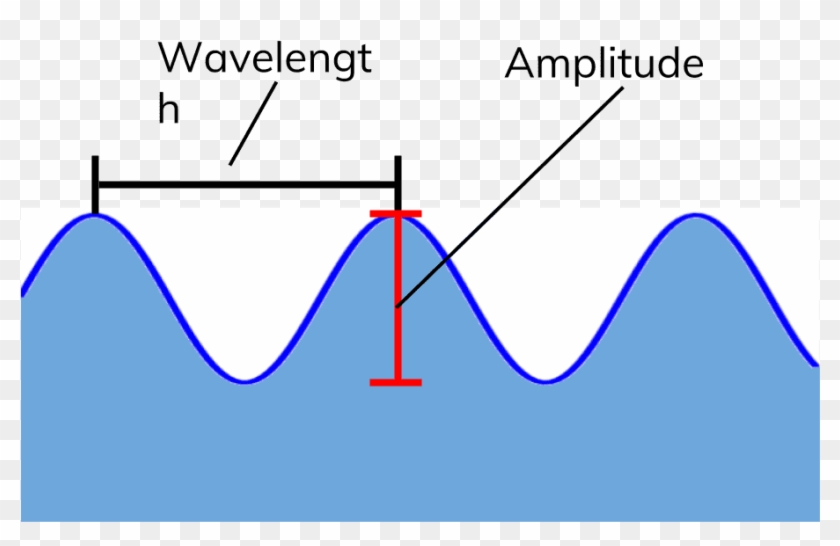
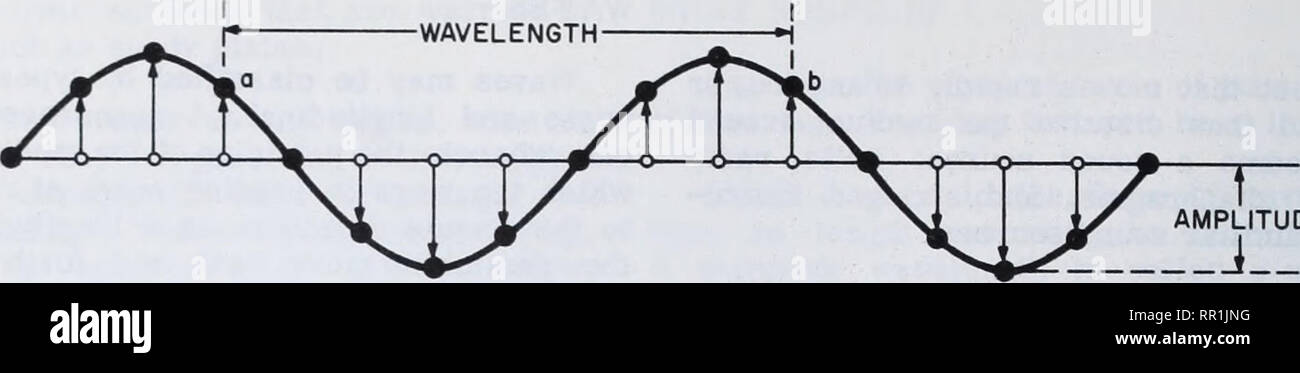
Longitudinal waves - Properties of waves - Eduqas - BBC Bitesize Waves transfer energy but not matter. Waves may be transverse (eg water wave) or longitudinal (eg sound wave). Wave motion can be described using the terms amplitude, wavelength, frequency and period. Longitudinal Wave - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Longitudinal or compression waves are defined as waves where the particle motion is in the same direction in which the wave is propagating. The oscillations in pressure are sinusoidal in nature and are characterised by their frequency, amplitude and wavelength ( Figure 9.1 ). Sign in to download full-size image Figure 9.1.
Longitudinal Wave: Definition, Parts & Examples - Study.com A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the disturbance moves in the same direction as the propagation of the wave. Going back to the Slinky example, the medium is the slinky, and the disturbance is...
Longitudinal wave labled
Longitudinal wave - Wikipedia Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation. GCSE PHYSICS - What is a Longitudinal Wave? - GCSE SCIENCE When a longitudinal wave moves through a material, the particles of the material move backwards and forwards along the direction in which the wave is travelling. Below is a picture of a longitudinal wave travelling along a spring. What is the Wavelength of a Longitudinal Wave? The wavelength of a longitudinal wave can be measured Parts And Types of A Wave - The Science Of Waves The wavelength of a transverse wave is the spatial period, or space, of the wave; the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. So basically like crest to crest. There are two types of waves; Transverse and Longitudinal or Compression Waves. Longitudinal Waves have different parts, however. The part of a longitudinal wave is called ...
Longitudinal wave labled. PDF Longitudinal waves - Harvard University LONGITUDINAL WAVES For atransversewave,ˆis the transverse displacement, so Fig. 1 is what the string actuallylookslike from the side. The wave is therefore very easy to visualize { you just need to look at the flgure. It's also fairly easy to see what the various points in Fig. 1 are doing as the wave travels to the right. 2022 Guidelines of the Taiwan Society of Cardiology and the … 01.03.2022 · The current automated BP monitors utilize oscillometric pressure wave amplitude during cuff deflation or inflation to determine SBP and DBP. 102 The irregular R-R interval in AF results in less accurate BP values in these patients. How to measure BP in AF patients accurately remains challenging. It has been shown that increasing the number of consecutive … longitudinal wave | physics | Britannica In a longitudinal wave, each particle of matter vibrates about its normal rest position and along the axis of propagation, and all particles participating in the wave motion behave in the same manner, except that there is a progressive change in phase ( q.v.) of vibration— i.e., each particle completes its cycle of reaction at a later time. Longitudinal wave - Labelled diagram - Wordwall Longitudinal wave. Share Share by Misshutchinson. KS4 Physics Science. Show More. Like. Edit Content. Embed. More. Leaderboard. Show more Show less . This leaderboard is currently private. Click Share to make it public. This leaderboard has been disabled by the resource owner. This leaderboard is disabled as your options are different to the ...
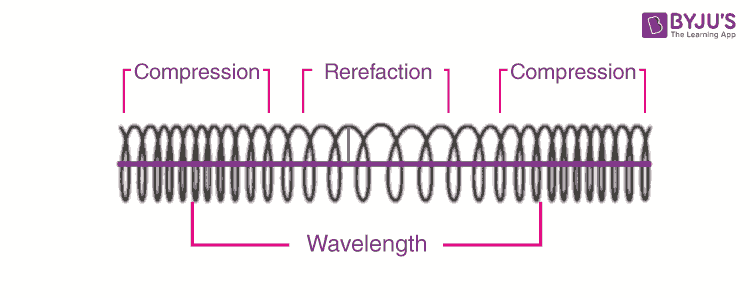
9.2 Compression and rarefaction | Longitudinal waves | Siyavula A rarefaction is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are furthest apart. As seen in Figure 9.2, there are regions where the medium is compressed and other regions where the medium is spread out in a longitudinal wave. The region where the medium is compressed is known as a compression and the region where the medium is spread ... Longitudinal Waves and Labelling wave diagrams - YouTube Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave diagram.This video an... Longitudinal Wave - Definition, Examples, Formula, Diagram - BYJUS Longitudinal waves are waves where the displacement of the medium is in the same direction as the direction of the travelling wave. The distance between the centres of two consecutive regions of compression or the rarefaction is defined by wavelength, λ. Longitudinal Wave Label Lesson Plans & Worksheets In this wave worksheet, students use Slinky's to observe the properties of waves. They observe longitudinal waves, transverse waves, traveling waves and standing waves and record their observations. They calculate the frequency and... + Lesson Planet: Curated OER From Vibration to Sound For Teachers 5th - 8th
Longitudinal Wave Label Diagram | Quizlet morgan_sanders25. AST 1002 Final Exam 2019. 60 terms. isabellarl515. Psychology Midterm 1b. 37 terms. tanyaaakay. Upgrade to remove ads. Only $35.99/year. Access Denied - LiveJournal Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu. 1.1: Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - Physics LibreTexts Sound is a longitudinal compression-expansion wave in a fluid. The wave speed for sound in an ideal gas is 1 ∕ 2c = (γRTabs) where γ and R are constants and T abs is the absolute temperature . The absolute temperature is measured in Kelvins and is numerically given by Tabs = TC + 273 ∘ where T C is the temperature in Celsius degrees. Longitudinal Wave - Explanation, Examples and FAQs - VEDANTU Depending on the type of motion two forms of waves are classified, the first one is a longitudinal wave and the second is a Transverse wave. The longitudinal motion or the longitudinal wave are found when the energy has to be transmitted within the medium. Whereas the transverse waves are formed at the surface. Terms Used in Longitudinal Waves
Longitudinal Wave Examples, Parts & Diagram | Amplitude of a ... The amplitude of a longitudinal wave refers to the distance between the particles in the areas where it is compressed. Thus, the denser or closer the particles are to each other, the higher the...
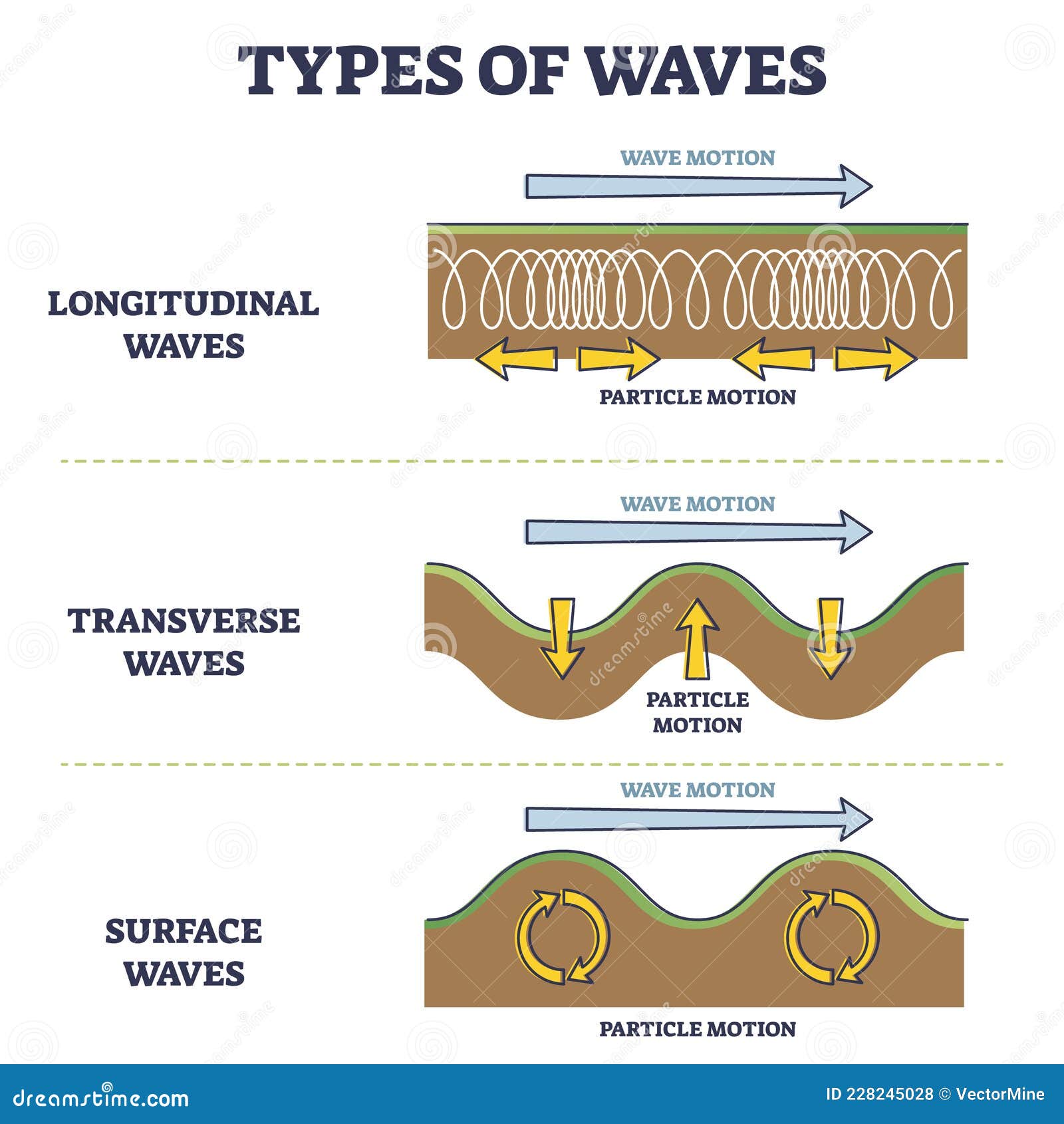
Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Motion - Pennsylvania State University Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Motion Mechanical Waves are waves which propagate through a material medium (solid, liquid, or gas) at a wave speed which depends on the elastic and inertial properties of that medium. There are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
Longitudinal wave- label Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Longitudinal wave- label. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Longitudinal waves - Transverse and longitudinal waves - AQA - GCSE ... Longitudinal waves show areas of compression and rarefaction: compressions are regions of high pressure due to particles being close together rarefactions are regions of low pressure due to...
Parts And Types of A Wave - The Science Of Waves The wavelength of a transverse wave is the spatial period, or space, of the wave; the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. So basically like crest to crest. There are two types of waves; Transverse and Longitudinal or Compression Waves. Longitudinal Waves have different parts, however. The part of a longitudinal wave is called ...
GCSE PHYSICS - What is a Longitudinal Wave? - GCSE SCIENCE When a longitudinal wave moves through a material, the particles of the material move backwards and forwards along the direction in which the wave is travelling. Below is a picture of a longitudinal wave travelling along a spring. What is the Wavelength of a Longitudinal Wave? The wavelength of a longitudinal wave can be measured
Longitudinal wave - Wikipedia Longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel ("along") to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation.


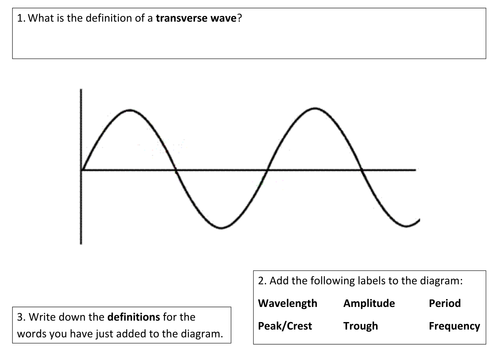

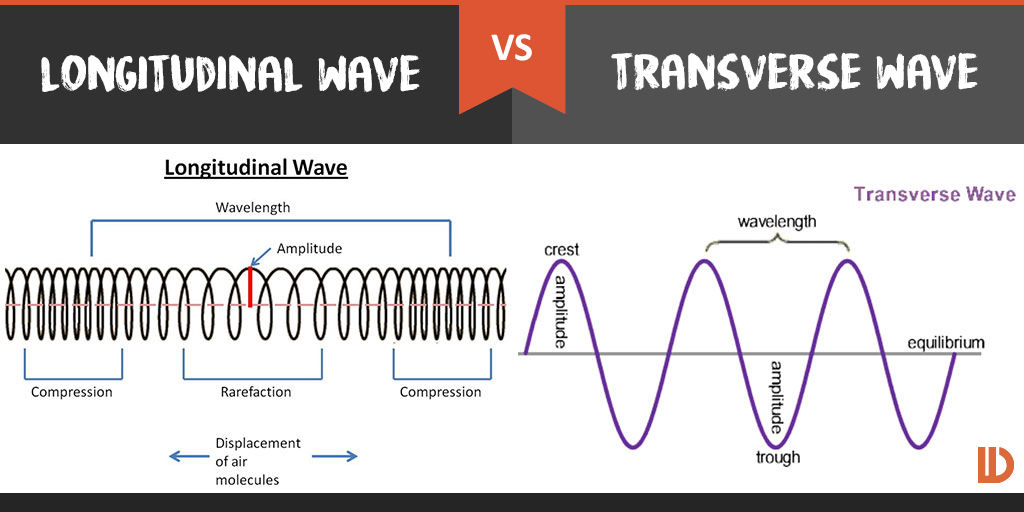





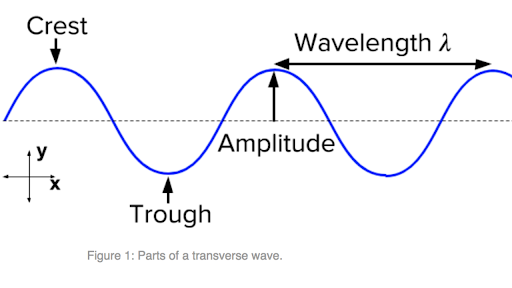
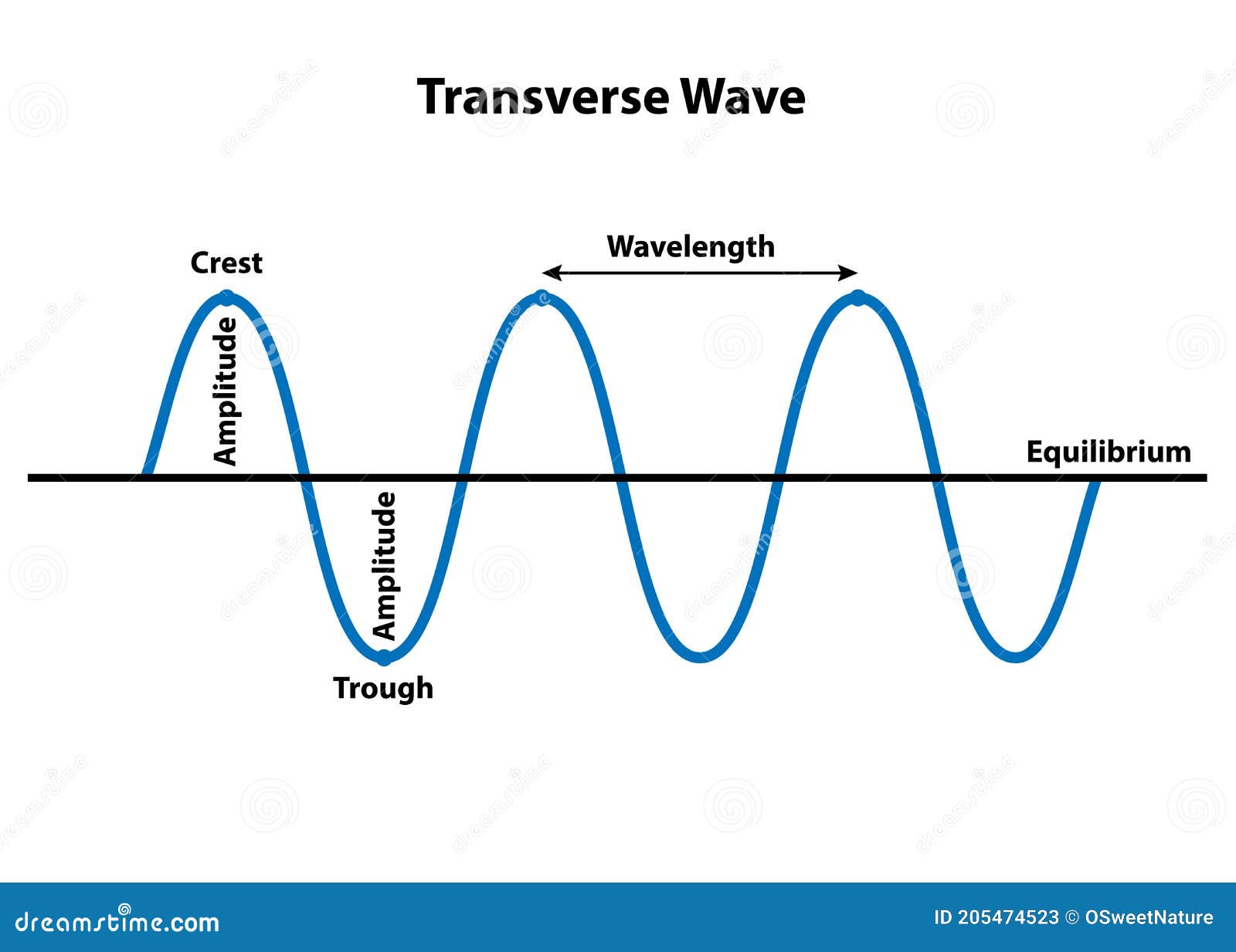
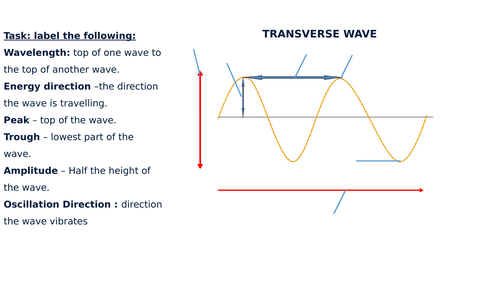







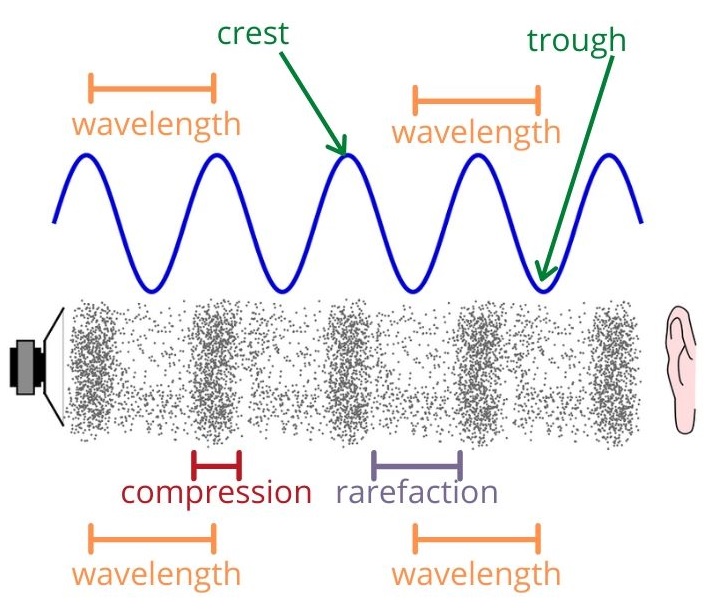



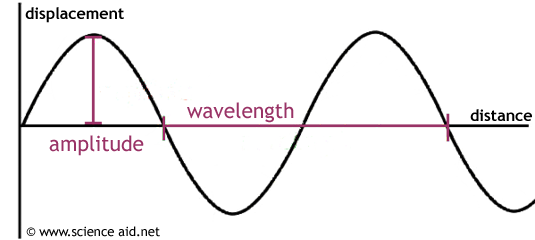



Post a Comment for "38 longitudinal wave labled"