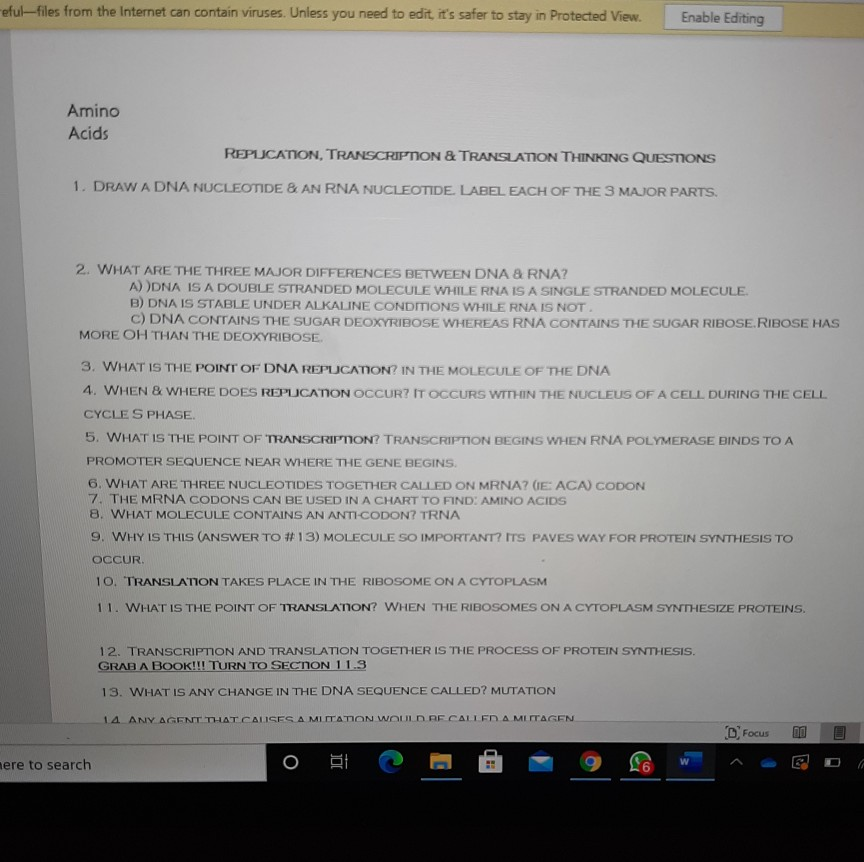
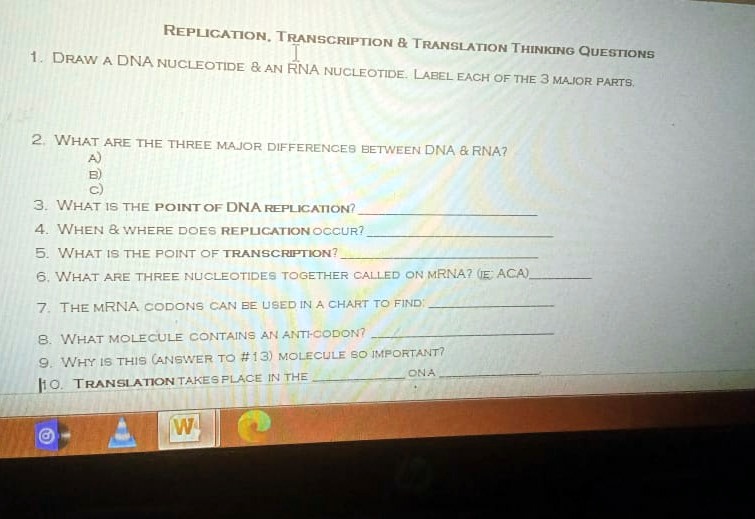
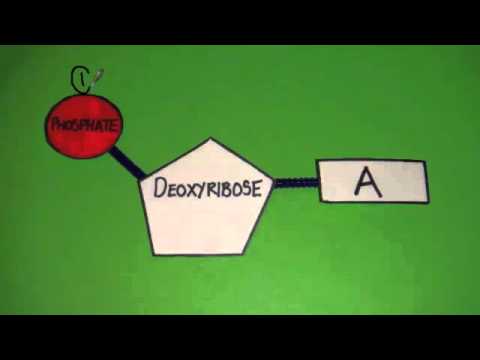
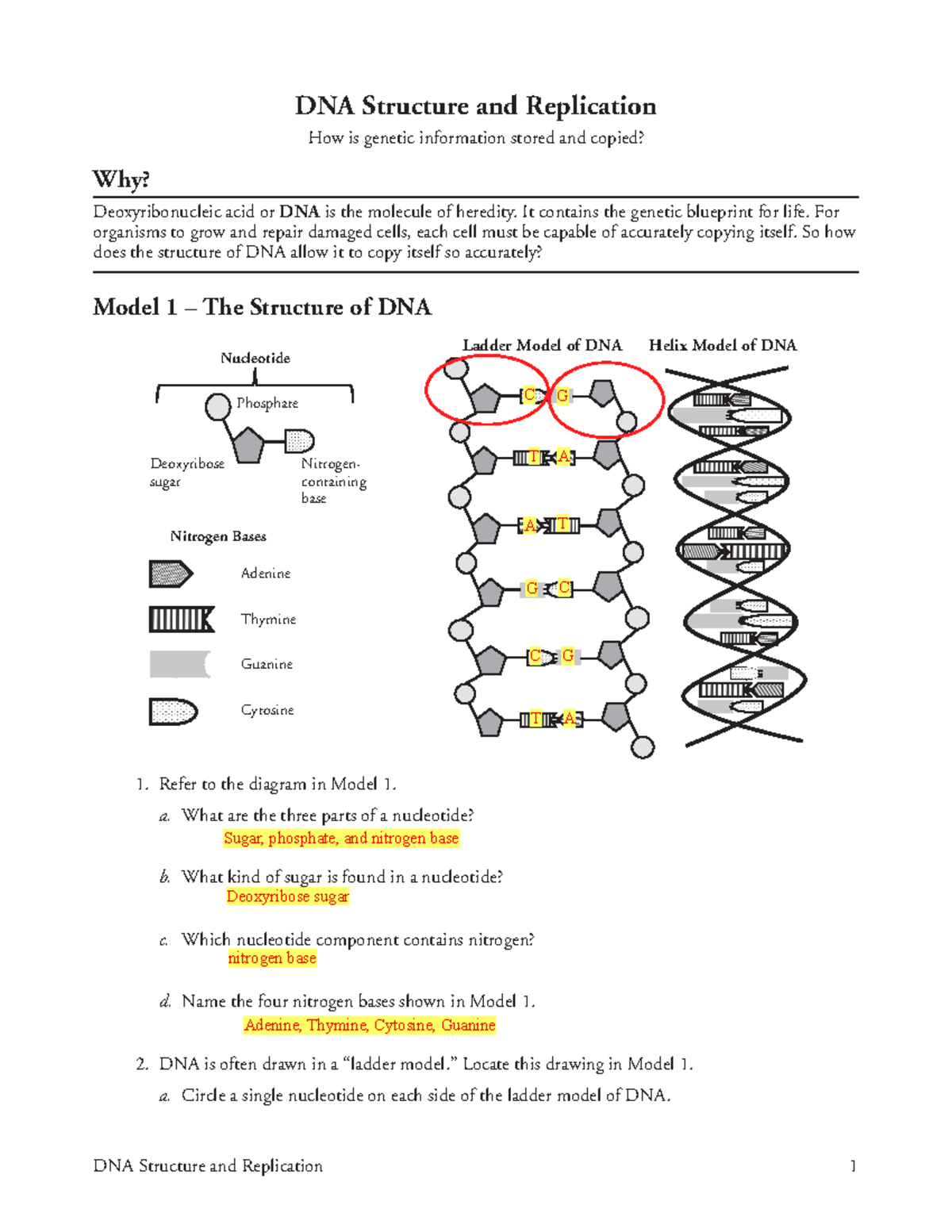
41 draw a single nucleotide. label the three parts
Answered: What if you were designing an… | bartleby Label the numbered parts of the… A: This picture represent the translation process which is the formation of polypeptide chain from… Q: In what part of chloroplasts do the coupled redox reactions occur? stroma membrane thylakoid… A: Introduction Plants and other living things employ a process called photosynthesis to change light… Q: An organism in a Domain also … Access Free Section Structure Of Dna 8 2 Study Guide structure is the same in all organisms. VOCABULARY nucleotide base pairing rules double helix MAIN IDEA: DNA is composed of four types of nucleotides. In the space below, draw a nucleotide and label its three parts using words and arrows. 1. How many types of nucleotides are present in ... SECTION STRUCTURE OF DNA 8.2 Study Guide - Quia
7 Types of RNA with Structure and Functions - Microbe Notes 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA): Structure and Functions. It is synthesized in the cell nucleus and then transported out of the cell to facilitate protein synthesis and code sequencing on proteins. The mRNA is translated into polypeptides. It comes in a wide range of sizes which reflects the polypeptide size it encodes.

Draw a single nucleotide. label the three parts
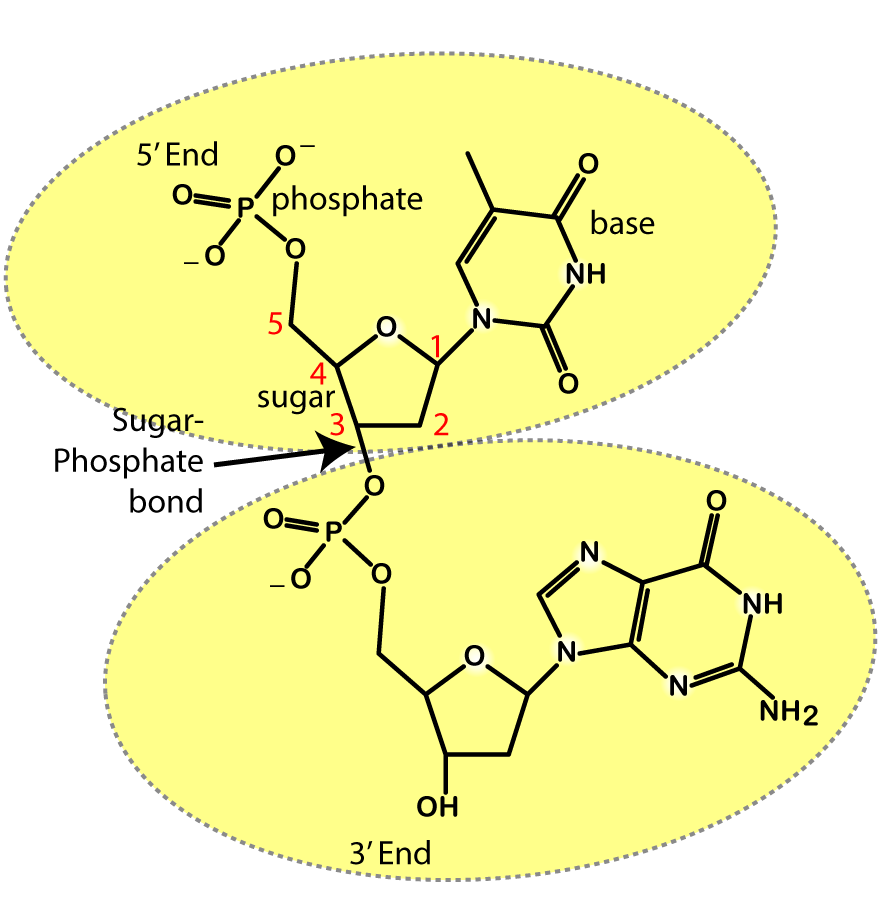
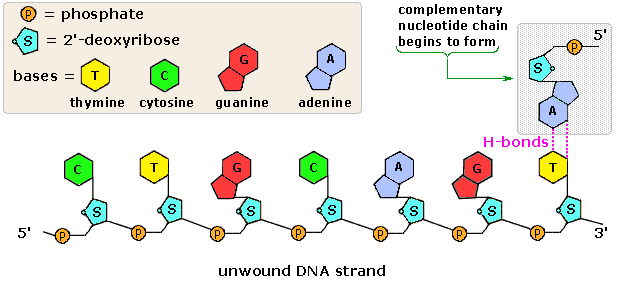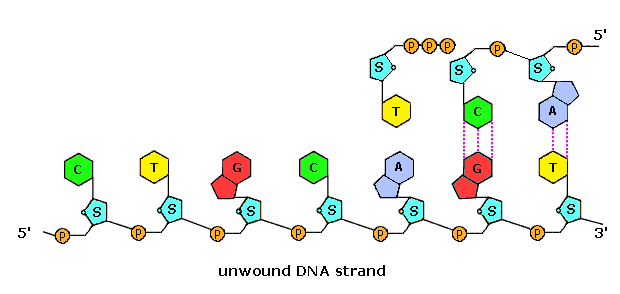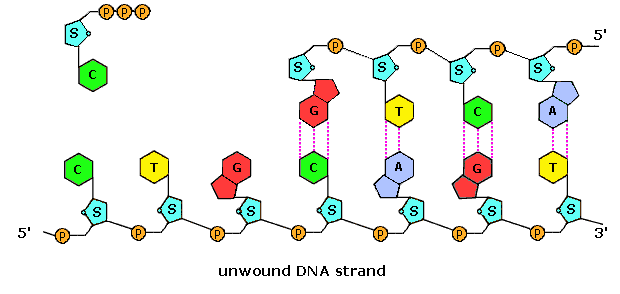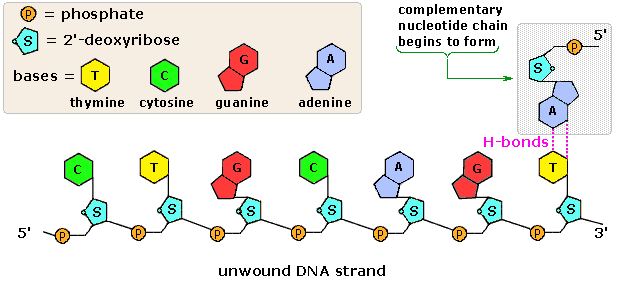
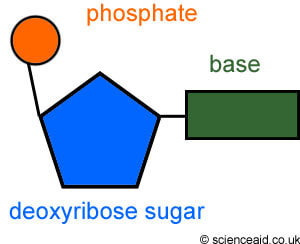
How To Draw A Double Stranded Dna Molecule - buddy-conaway Begin drawing additional pairs of parallel curved lines on the opposite diagonal from the first. If you are drawing by hand use a ruler. DNA drawing - step 3. Before DNA can be replicated the double stranded molecule must be unzipped into two single strands. Shown below is a double-stranded bacterial E. Nucleotides, DNA, and RNA - Knowledge @ AMBOSS The genetic information of an organism is stored in the form of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are long linear polymers composed of nucleotide building blocks. Each nucleotide is comprised of a sugar, a phosphate residue, and a nitrogenous bases (a purine or pyrimidine). DNA is longer than RNA and contains the entire genetic information of ... 2.5: DNA Replication - Biology LibreTexts Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (a 5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate group. The nucleotide is named according to its nitrogenous base, purines such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or pyrimidines such as cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Recall the structures below.
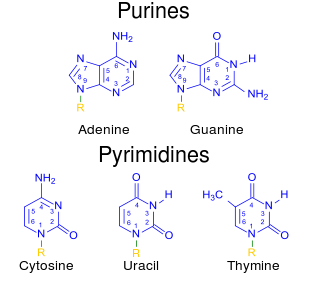
Draw a single nucleotide. label the three parts. Cell nucleus: Histology, structure and functions | Kenhub The cell nucleus is the most noticeable organelle within the eukaryotic cell, and perhaps the most important and defining feature of the eukaryotic cells.Most of the genetic material (DNA) is contained in the nucleus, while a small amount of it is found in mitochondria. The majority of human cells have a single nucleus, although there are several cell types that have multiple nuclei (e.g ... Dna Replication Labeling Worksheet - Craftity Draw and label a nucleotide (3 main parts) (a simple diagram is sufficient). Structure 1 on the diagram. The consistent alternation of amino acids emerges from the top of the. Using what you now know of dna structure and. Double Helix - Genome.gov Double helix, as related to genomics, is a term used to describe the physical structure of DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of two linked strands that wind around each other to resemble a twisted ladder in a helix-like shape. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Nucleotides are made up of 3 parts. The first is a distinct nitrogenous base, which is adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. These nitrogenous bases are either purines or pyrimidines. Base pairs are formed when adenine forms a hydrogen bond with thymine, or cytosine forms a hydrogen bond with guanine.
Answered: A perfect flower is one in which both… | bartleby It is following three… question_answer. Q: 1. Immunization of laboratory personnel for infectious agent(s) they are working with is an example… A: Immunization It is the process of giving a vaccine to a person through which the immune system of… question_answer. Q: A 32-year-old woman comes to the office with her 2-year-old son, whom you have been treating for… A: … learn.genetics.utah.edu › content › basicsBasic Genetics - University of Utah To read a set of chromosomes, scientists look for key features to identify their similarities and differences. How to Draw a Plasmid Map - The Official Blog of Edvotek® Draw the next site X+Y spaces from the 0/start space when Y equals the size of the second smallest fragment. Continue until you've accounted for all the fragments. It's also useful to label the distances between cuts sites (i.e. the numbers X and Y) on the side. 5) Examine the other single enzyme digestions. Chapter 10 - Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis - CHE 120 ... Identify the three molecules needed to form the nucleotides in each nucleic acid. a. DNA b. RNA 2. Classify each compound as a pentose sugar, a purine, or a pyrimidine. a. adenine b. guanine c. deoxyribose d. thymine e. ribose f. cytosine Answers 1. a. nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine), 2-deoxyribose, and H 3 PO 4
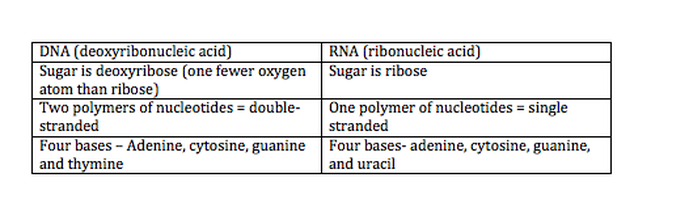
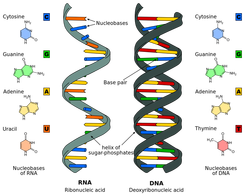
7 Monomers of DNA and RNA | Their Chemistry and Structure - Study Read Monomers are single-unit molecules that can bind to each other to form long chains or polymers. The monomers of DNA and RNA are Ribose sugar molecule Deoxyribose sugar molecule Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine Uracil What Is DNA? Summary, Structure, and Importance - Healthline Each nucleotide contains three components: a sugar a phosphate group a nitrogen base The sugar in DNA is called 2-deoxyribose. These sugar molecules alternate with the phosphate groups, making up... DNA Translation - Initiation - Elongation - TeachMePhysiology Translation is the process by which the genetic code contained within a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule is decoded to produce a specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.It occurs in the cytoplasm following DNA transcription and, like transcription, has three stages: initiation, elongation and termination. In this article we will discuss the components and stages of DNA translation. ViennaRNA Tutorial - Theoretical Biochemistry Group 02/08/2017 · Draw and markup RNA secondary structures in PostScript, SVG, or GML ... Each sequence must appear as a single line in the file without embedded white spaces. A sequence may be preceded by a special line starting with the ‘>’ character followed by a sequence name. This name will be used by the programs in the ViennaRNA Package as basename for the …
› patents › basicsNonprovisional (Utility) Patent Application Filing Guide | USPTO A very long view may be divided into several parts placed one above the other on a single sheet. However, the relationship between the different parts must be clear and unambiguous. Sectional Views. The plane on which a sectional view is taken should be indicated by a broken line on the view from which the section is cut.
Understanding a Genome Sequence - Genomes - NCBI Bookshelf 7.1. Locating the Genes in a Genome Sequence. Once a DNA sequence has been obtained, whether it is the sequence of a single cloned fragment or of an entire chromosome, then various methods can be employed to locate the genes that are present. These methods can be divided into those that involve simply inspecting the sequence, by eye or more frequently by computer, …
Dna Model: Types of DNA, Levels, Structure, Diagram - Embibe Each nucleotide is made up of a sugar termed deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogen-containing nucleobases (cytosine [C], guanine [G], adenine [A], or thymine [T]). This article covers the structure of DNA, types of DNA, etc. To know more about the DNA Model, scroll down the article. What is DNA?
Describe The Structure Of A Nucleotide - 314 Words | Studymode A nucleotide is a sugar molecule that has 3 parts including a simple sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Nucleotides join together forming long chains, with the phosphate group of nucleotide bonding to the deoxyribose sugar of an adjacent nucleotide. 3. Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is often described as a zipper.
› books › NBK19932Genetics and Health - Genes, Behavior, and the Social ... May 15, 2006 · An SNP is the DNA sequence variation that occurs when a single nucleotide (A, T, C, or G) in the genome sequence is altered (Smith, 2005). 2 A candidate gene is a gene whose protein product is involved in the metabolic or physiological pathways associated with a particular disease ( IOM, 2005 ).
What is a Polypeptide Chain - Definition, Types (Bond) and Examples The tertiary structure has three dimensional atom arrangement in a single polypeptide chain. The tertiary structure is maintained by disulfide bonds; which are formed between the side chains of cysteine. It is formed through the oxidation of two thiol groups thereby forming a disulfide bond. Quaternary structure
Polynucleotide Chain Structure & Overview - Study.com The building blocks of DNA and RNA are nucleotides that consist of the following components: Nitrogenous base (A base having a nitrogen atom) Nitrogenous bases are nitrogen-containing heterocyclic,...
B1140L U3 Study Guide 06-10-2022.pdf - UNIT 3: THE... A string of amino acids forms the primary structure of a protein. The string is called a poly PEPTIDE Nucleic Acids 1. List two types of nucleic acids. DNA AND RNA 2. DNA serves as…. (finish the sentence from the presentation). "The genetic blueprint for life" 3. People look different from each other because they have different proteins.
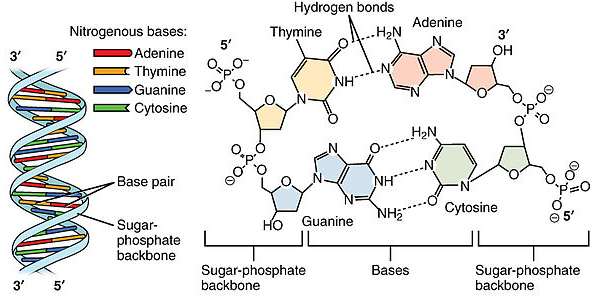
Watson and Crick DNA Model - Microbe Notes DNA Model. The three-dimensional structure of DNA, first proposed by James D. Watson and Francis H. C. Crick in 1953, consists of two long helical strands that are coiled around a common axis to form a double helix. Each DNA molecule is comprised of two biopolymer strands coiling around each other.
Nucleotide - Genome A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
Molecule Of Heredity Chapter 11 - 512 Words | Studymode Another enzyme bonds floating nucleotides to the single strands to make two new DNA. Each DNA will have an old strand and a new strand. RNA which is a nucleic acid, a nucleotide differs from DNA in three ways: 1. sugar is ribose; 2. there is a single strand of nucleotides, not two; 3. and uracil instead of thymine.
(Solved) - 1. Distinguish a purine from a pyrimidine, and identify ... 1- Draw a short segment ...
Basic Genetics - University of Utah Learn the essential roles of the three most plentiful types of RNA messenger, transfer, and ribosomal in the processes of transcription and translation. learn more. Beyond the Central Dogma. Learn about some of the less-known roles of RNA. Tour of Basic Genetics. video. What are Traits? Explore traits, the characteristics that make us unique. video. What are DNA & …
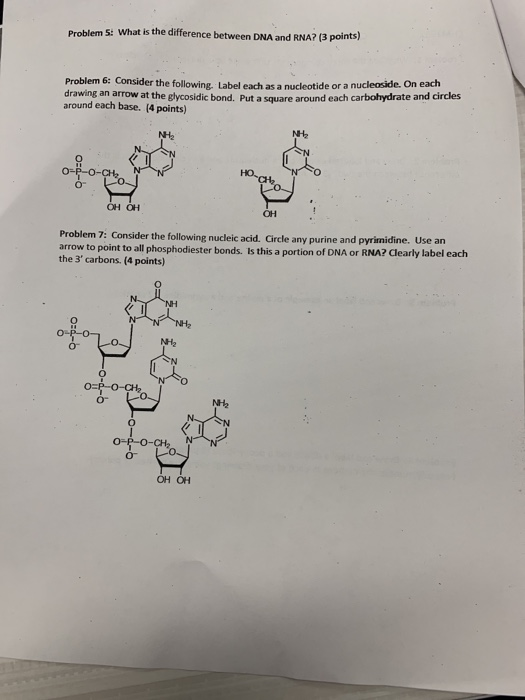
› en-za › documentLIFE Sciences Grade 12 Notes - LIFE SCIENCES GRADE ... - StuDocu 1. Label parts 1, 2 and 3 2. Give the number of nucleotides shown in the diagram 3. Name two places in an animal cell where this nucleic acid may be found. 4. What is the natural shape of this molecule? 5. Draw a nucleotide with the nitrogenous base adenine. RNA – ribonucleic acid. Key terminology
Cladogram- definition, features, parts, examples (vs Phylogram) Step 3: Generate a cladogram from the obtained data of the multiple sequence alignment The next step is to select a proper substitution model that provides estimates of the relationship between the organisms by taking into account the results of multiple sequence alignment.
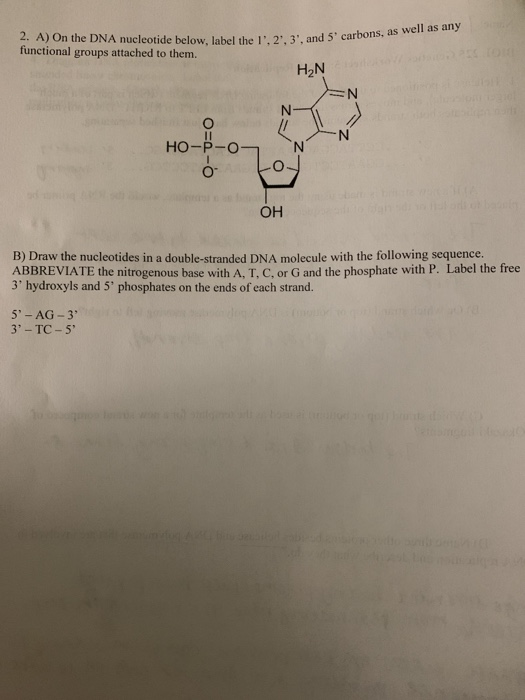
(Get Answer) - a) In DNA microarrays, the typical probe is~20 ... Similarities between tráf replication, transcription & translation thinking questions nucleotide & an rna nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 1. Draw a dna 2. What are the three major differences between d na & rna? A) b) c) 3. What is the...
1.3: Classification - The Three Domain System - Biology LibreTexts Phylogeny refers to the evolutionary relationships between organisms. The Three Domain System, proposed by Woese and others, is an evolutionary model of phylogeny based on differences in the sequences of nucleotides in the cell's ribosomal RNAs (rRNA), as well as the cell's membrane lipid structure and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
The Coot User Manual - MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology 1.6 Command Line Arguments. Rather that using the GUI to read in information, you can use the following command line arguments: --c cmd to run a command cmd on start up --script filename to run a script on start up (but see Section Scripting) --no-state-script don’t run the 0-coot.state.scm script on start up. Don’t save a state script on exit either.
› questions-and-answers › a-perfectAnswered: A perfect flower is one in which both… | bartleby Q: Shown below are single-stranded DNA probe and target sequences. Where on the target sequence will… Where on the target sequence will… A: In cells, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid that functions as the original blueprint…
Nucleosome: Definition & Structure - Video & Lesson Transcript - Study.com The core particle has eight total histones. One H2A and H2B bind together to form a dimer, or two proteins bound together. An H3 and an H4 will bind to also form a dimer. Next, one H3/H4 dimer...
› questions-and-answers › what-ifAnswered: What if you were designing an… | bartleby Science Biology Q&A Library What if you were designing an experiment testing the impact of different pH levels on plant growth. What would be the levels of your independent variable and you would need to vary the pH of a factor that plants need for growth such as soil, fertilizer, or water.
Genetics and Health - Genes, Behavior, and the Social Environment ... 15/05/2006 · Although there are many possible causes of human disease, family history is often one of the strongest risk factors for common disease complexes such as cancer, cardiovascular disease (CVD), diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and psychiatric illnesses. A person inherits a complete set of genes from each parent, as well as a vast array of cultural and socioeconomic …
Biochemistry Questions and Answers | Homework.Study.com Draw two and three-dimensional structures of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acid. View Answer Mimi s daily caloric consumption consists of three meals: Breakfast: 173 kcal; 12 g protein, 20 g carbohydrates, 5 g fat Lunch: 254 kcal, 15 g …
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia The DNA of a prokaryotic cell consists of a single circular chromosome that is in direct contact with the cytoplasm. The nuclear region in the cytoplasm is called the nucleoid. Most prokaryotes are the smallest of all organisms ranging from 0.5 to 2.0 μm in diameter. A prokaryotic cell has three regions:
Graphical View Legend - National Center for Biotechnology Information Up to three insertions are reported in a single tooltip. The tooltip can be "pinned" using the pushpin on the top left. All information provided in the tooltip can be highlighted and copied to the clipboard. Clicking on the magnifying glass on the top resets the graphical view around the selected feature.
LIFE Sciences Grade 12 Notes - LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 NOTES 1 … 1. Label parts 1, 2 and 3 2. Give the number of nucleotides shown in the diagram 3. Name two places in an animal cell where this nucleic acid may be found. 4. What is the natural shape of this molecule? 5. Draw a nucleotide with the nitrogenous base adenine. RNA – …
Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea, two of the three domains of life.Prokaryotic cells were the first form of life on Earth, characterized by having vital biological processes including cell signaling.They are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and lack a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The DNA of a prokaryotic cell consists of a single circular …
2.5: DNA Replication - Biology LibreTexts Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose (a 5-carbon sugar), and a phosphate group. The nucleotide is named according to its nitrogenous base, purines such as adenine (A) and guanine (G), or pyrimidines such as cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Recall the structures below.
Nucleotides, DNA, and RNA - Knowledge @ AMBOSS The genetic information of an organism is stored in the form of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are long linear polymers composed of nucleotide building blocks. Each nucleotide is comprised of a sugar, a phosphate residue, and a nitrogenous bases (a purine or pyrimidine). DNA is longer than RNA and contains the entire genetic information of ...
How To Draw A Double Stranded Dna Molecule - buddy-conaway Begin drawing additional pairs of parallel curved lines on the opposite diagonal from the first. If you are drawing by hand use a ruler. DNA drawing - step 3. Before DNA can be replicated the double stranded molecule must be unzipped into two single strands. Shown below is a double-stranded bacterial E.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)

![Location of the nucleotides labeled by [5-32 P] (2N 3 A76 ...](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/12360024/figure/fig3/AS:460533083185171@1486811051723/Location-of-the-nucleotides-labeled-by-5-32-P-2N-3-A76tRNA-Phe-arrows-in-the-3-half.png)








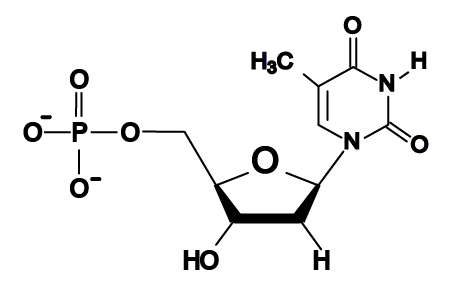


Post a Comment for "41 draw a single nucleotide. label the three parts"